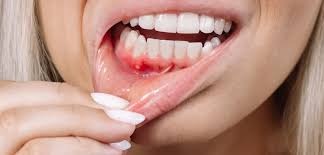
Tooth infections are not only painful but can also lead to serious health complications if left untreated. One of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics for treating such infections is Amoxicillin. Understanding the right amoxicillin dose for a dental infection is essential to ensure safe and effective treatment. In this article from Dental Advice Today, we’ll cover everything you need to know about using amoxicillin for oral infections—its dosage, duration, side effects, and precautions.
What Is a Tooth or Dental Infection?
A tooth infection, also known as a dental abscess, occurs when bacteria invade the inner parts of a tooth or the surrounding gums. This can happen due to untreated cavities, cracked teeth, or poor oral hygiene. When bacteria multiply, they cause pus buildup, swelling, and pain. In such cases, understanding the dental infection amoxicillin dose is essential, as timely antibiotic treatment helps control the infection and prevent it from spreading.
Common symptoms of a dental infection include:
- Throbbing or sharp tooth pain
- Swollen gums or face
- Sensitivity to hot or cold
- Fever or general weakness
- Foul taste in the mouth due to pus discharge
In such cases, antibiotics like amoxicillin are prescribed to fight the bacterial infection and prevent it from spreading.
Why Is Amoxicillin Prescribed for Dental Infections?
Amoxicillin belongs to the penicillin family of antibiotics and is widely used to treat bacterial infections, including those in the mouth and gums. According to Dental Advice Today experts, amoxicillin is often the first-line antibiotic choice because it:
- Is highly effective against most oral bacteria
- Works quickly to reduce pain and swelling
- Has fewer side effects compared to other antibiotics
- Is affordable and easily available
However, it is important to note that antibiotics alone don’t fix the underlying dental issue. They only help control the infection until proper dental treatment—such as root canal therapy or tooth extraction—is performed.
How Amoxicillin Works
Amoxicillin works by targeting and weakening the bacterial cell walls, causing the bacteria to break apart and die. This stops the infection from spreading and allows your body’s immune system to recover.
When prescribed at the correct dose and taken for the full course, amoxicillin can effectively eliminate bacteria responsible for dental abscesses and gum infections.
Recommended Amoxicillin Dose for Dental Infection
Determining the right amoxicillin dose for a tooth infection depends on several factors, including age, weight, infection severity, and medical history. However, dentists typically follow standard dosage guidelines.
For Adults
- Standard dose: 500 mg every 8 hours (three times daily)
- Alternative dose: 875 mg every 12 hours (twice daily)
The course usually lasts 5 to 7 days, but in severe cases, it may be extended up to 10 days. Always complete the full course prescribed by your dentist, even if symptoms improve earlier.
For Children
Children’s doses are based on body weight:
- 20–40 mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into doses every 8 hours.
A dentist or pediatrician will calculate the exact dosage for children to ensure safety.
When Amoxicillin Alone May Not Be Enough
Sometimes, if the infection is resistant or severe, your dentist might prescribe amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (Augmentin). This combination prevents bacteria from becoming resistant to amoxicillin and enhances its effectiveness.
Typical adult dosage: 875 mg/125 mg every 12 hours for 5–10 days.
Dental Advice Today recommends using this combination only when advised by a qualified dentist, as unnecessary antibiotic use can lead to bacterial resistance.
Signs That Amoxicillin Is Working
You should start noticing improvement within 2–3 days of starting amoxicillin. Signs of recovery include:
- Reduced pain and swelling
- Lower temperature if you had a fever
- Decreased gum tenderness
- Improvement in general comfort and ability to chew
If your symptoms don’t improve after three days, or if they worsen, contact your dentist immediately. The bacteria may be resistant, or the infection might need drainage or other dental treatment.
Side Effects of Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, but like all antibiotics, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include:
- Mild diarrhea or stomach upset
- Nausea or vomiting
- Skin rash or itching
- Yeast infections (in women)
Serious but rare reactions include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Severe rash or swelling
- Persistent diarrhea
If you experience any severe reaction, stop the medication and seek medical help immediately.
Important Safety Precautions
Before taking amoxicillin for a dental infection, keep these points in mind:
- Allergies: If you are allergic to penicillin or any antibiotic in the same class, inform your dentist immediately. Alternatives like clindamycin or azithromycin may be prescribed instead.
- Medical Conditions: Tell your dentist if you have kidney disease, asthma, or a history of antibiotic-related colitis.
- Drug Interactions: Amoxicillin can interact with birth control pills, anticoagulants (like warfarin), and other antibiotics.
- Complete the Course: Never stop antibiotics early, even if you feel better. Stopping too soon may allow bacteria to regrow.
- Avoid Overuse: Overusing antibiotics can lead to bacterial resistance, making future infections harder to treat.
Alternative Antibiotics for Dental Infections
While amoxicillin is the most commonly prescribed antibiotic, some patients may require alternatives. According to Dental Advice Today, other effective options include:
- Clindamycin: Used for patients allergic to penicillin; effective against anaerobic bacteria.
- Metronidazole: Often combined with amoxicillin for deeper infections.
- Azithromycin: Another alternative with fewer doses needed per day.
The choice of antibiotic depends on the type and severity of infection, as well as patient tolerance.
When to See a Dentist
While antibiotics help control infection, they are not a permanent fix. You must see a dentist to address the root cause of the infection.
Visit your dentist if you experience:
- Persistent or increasing pain
- Facial swelling or difficulty swallowing
- Fever or swollen lymph nodes
- Recurring dental abscesses
Delaying dental treatment can allow the infection to spread to your jaw, sinuses, or bloodstream—a serious condition requiring emergency care.
Key Points to Remember
- Dental infection amoxicillin dose for adults is usually 500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours.
- The typical treatment duration is 5–7 days.
- Always complete the full course as prescribed.
- Don’t rely solely on antibiotics—see a dentist for proper treatment.
- Consult a dentist or doctor before taking antibiotics, especially if you have allergies or medical conditions.
Conclusion
The right amoxicillin dose for a tooth infection depends on your condition and your dentist’s prescription. While amoxicillin effectively treats bacterial dental infections, it should never replace proper dental care. Following your dentist’s instructions, completing the antibiotic course, and maintaining good oral hygiene are key steps to a full recovery.
At Dental Advice Today, we emphasize safe antibiotic use and regular dental visits to prevent complications. Remember, early treatment and proper medication can protect not just your teeth—but your overall health.